Again in highschool chemistry, I bear in mind ready with my bench accomplice for crystals to kind on our stick within the cup of blue resolution. Different teams round us jumped with pleasure when their crystals shaped, however my group simply waited. When the bell rang, everybody left however me. My instructor came visiting, picked up an unopened bag on the counter and instructed me, “Crystals can’t grow if the salt is not in the solution.”
To me, this was how science labored: What you anticipate to occur is obvious and concrete. And if it doesn’t occur, you’ve accomplished one thing incorrect.
If solely it had been that straightforward.
It took me a few years to understand that science is not only some sequence of actions the place you understand what’s going to occur on the finish. As a substitute, science is about discovering and producing new data.
Now, I’m a psychologist learning how scientists do science. How do new strategies and instruments get adopted? How do modifications occur in scientific fields, and what hinders modifications in the way in which we do science?
One apply that has fascinated me for a few years is replication analysis, the place a analysis group tries to redo a earlier research. Like with the crystals, getting the identical consequence from completely different groups doesn’t at all times occur, and whenever you’re on the workforce whose crystals don’t develop, you don’t know if the research didn’t work as a result of the speculation is incorrect, or whether or not you forgot to place the salt within the resolution.
The replication disaster
A Could 2025 government order by President Donald Trump emphasised the “reproducibility crisis” in science. Whereas replicability and reproducibility could sound related, they’re distinct.
Reproducibility is the flexibility to make use of the identical information and strategies from a research and reproduce the consequence. In my editorial function on the journal Psychological Science, I conduct computational reproducibility checks the place we take the reported information and verify that each one the leads to the paper will be reproduced independently.
However we’re not working the research over once more, or amassing new information. Whereas reproducibility is necessary, analysis that’s incorrect, fallible and generally dangerous can nonetheless be reproducible.
Against this, replication is when an impartial workforce repeats the identical course of, together with amassing new information, to see in the event that they get the identical outcomes. When analysis replicates, the workforce will be extra assured that the outcomes aren’t a fluke or an error.
Reproducibility and replicability are each necessary, however have key variations.
Open Economics Information, CC BY
The “replication crisis,” a time period coined in psychology within the early 2010s, has unfold to many fields, together with biology, economics, medication and pc science. Failures to duplicate high-profile research concern many scientists in these fields.
Why replicate?
Replicability is a core scientific worth: Researchers need to have the ability to discover the identical consequence repeatedly. Many necessary findings aren’t revealed till they’re independently replicated.
In analysis, likelihood findings can happen. Think about if one individual flipped a coin 10 occasions and acquired two heads, then instructed the world that “coins have a 20% chance of coming up heads.” Though that is an unlikely end result – about 4% – it’s potential.
Replications can appropriate these likelihood outcomes, in addition to scientific errors, to make sure science is self-correcting.
For instance, within the seek for the Higgs boson, two analysis facilities at CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Analysis, ATLAS and CMS, independently replicated the detection of a particle with a big distinctive mass, resulting in the 2013 Nobel Prize in physics.
The ATLAS experiment on the Giant Hadron Collider at CERN is certainly one of two that led to the invention of the Higgs boson.
CERN, CC BY
The preliminary measurements from the 2 facilities really estimated the mass of the particle as barely completely different. So whereas the 2 facilities didn’t discover similar outcomes, the groups evaluated them and decided they had been shut sufficient. This variability is a pure a part of the scientific course of. Simply because outcomes aren’t similar doesn’t imply they aren’t dependable.
Analysis facilities like CERN have replication constructed into their course of, however this isn’t possible for all analysis. For initiatives which might be comparatively low price, the unique workforce will typically replicate their work previous to publication – however doing so doesn’t assure that an impartial workforce may get the identical outcomes.
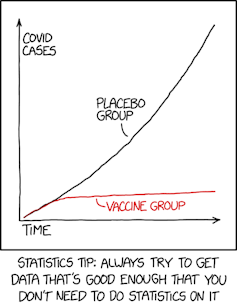
As a result of the outcomes on vaccine efficacy had been so clear, replication wasn’t crucial and would have slowed the method of getting the vaccine to folks.
XKCD, CC BY-NC
When initiatives are expensive, pressing or time-specific, independently replicating them previous to disseminating outcomes is commonly not possible. Bear in mind when folks throughout the nation had been ready for a COVID-19 vaccine?
The preliminary Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine took 13 months from the beginning of the trial to authorization from the Meals and Drug Administration. The outcomes of the preliminary research had been so clear and convincing {that a} replication would have unnecessarily delayed getting the vaccine out to the general public and slowing the unfold of illness.
Since not each research will be replicated previous to publication, it’s necessary to conduct replications after research are revealed. Replications assist scientists perceive how effectively analysis processes are working, establish errors and self-correct. So what’s the method of conducting a replication?
The replication course of
Researchers may independently replicate the work of different groups, like at CERN. And that does occur. However when there are solely two research – the unique and the replication – it’s exhausting to know what to do after they disagree. For that cause, giant multigroup groups typically conduct replications the place they’re all replicating the identical research.
Alternatively, if the aim is to estimate the replicability of a physique of analysis – for instance, most cancers biology – every workforce may replicate a unique research, and the main target is on the share of research that replicate throughout many research.
These large-scale replication initiatives have arisen world wide and embrace ManyLabs, ManyBabies, Psychological Accelerator and others.
Replicators begin by studying as a lot as potential about how the unique research was carried out. They’ll acquire particulars concerning the research from studying the revealed paper, discussing the work with its unique authors and consulting on-line supplies.
The replicators need to know the way the individuals had been recruited, how the information was collected and utilizing what instruments, and the way the information was analyzed.
However generally, research could omit necessary particulars, just like the questions individuals had been requested or the model of kit used. Replicators need to make these tough choices themselves, which might have an effect on the end result.
Replicators additionally typically explicitly change particulars of the research. For instance, many replication research are carried out with bigger samples – extra individuals – than the unique research, to make sure the outcomes are dependable.
Registration and publication
Sadly, replication analysis is difficult to publish: Solely 3% of papers in psychology, lower than 1% in schooling and 1.2% in advertising and marketing are replications.
If the unique research replicates, journals could reject the paper as a result of there isn’t any “new insight.” If it doesn’t replicate, journals could reject the paper as a result of they assume the replicators made a mistake – bear in mind the salt crystals.
Due to these points, replicators typically use registration to strengthen their claims. A preregistration is a public doc describing the plan for the research. It’s time-stamped to earlier than the research is carried out.
One of these doc improves transparency by making modifications within the plan detectable to reviewers. Registered studies take this a step additional, the place the analysis plan is topic to see evaluate earlier than conducting the research.
If the journal approves the registration, they decide to publishing the outcomes of the research whatever the outcomes. Registered studies are perfect for replication analysis as a result of the reviewers don’t know the outcomes when the journal commits to publishing the paper, and whether or not the research replicates or not gained’t have an effect on whether or not it will get revealed.
About 58% of registered studies in psychology are replication research.
Replication analysis typically makes use of the very best requirements of analysis apply: giant samples and registration. Whereas not all replication analysis is required to make use of these practices, people who do contribute drastically to our confidence in scientific outcomes.
Replication analysis is a helpful thermometer to know if scientific processes are working as supposed. Lively dialogue of the replicability disaster, in each scientific and political areas, suggests to many researchers that there’s room for progress. Whereas no subject would anticipate a replication price of 100%, new processes amongst scientists intention to enhance the charges from these prior to now.



