The Solar will sometime die. This can occur when it runs out of hydrogen gasoline in its core and may not produce vitality by nuclear fusion because it does now. The dying of the Solar is usually considered the top of the photo voltaic system. However in actuality, it might be the start of a brand new part of life for all of the objects residing within the photo voltaic system.
When stars just like the Solar die, they undergo a part of speedy enlargement referred to as the Purple Large part: The radius of the star will get larger, and its shade will get redder. As soon as the gravity on the star’s floor is not robust sufficient for it to carry on to its outer layers, a big fraction – as much as about half – of its mass escapes into area, abandoning a remnant referred to as a white dwarf.
I’m a professor of astronomy on the College of Wisconsin-Madison. In 2020, my colleagues and I found the primary intact planet orbiting round a white dwarf. Since then, I’ve been fascinated by the prospect of life on planets round these, tiny, dense white dwarfs.
Researchers seek for indicators of life within the universe by ready till a planet passes between a star and their telescope’s line of sight. With mild from the star illuminating the planet from behind, they will use some easy physics ideas to find out the kinds of molecules current within the planet’s environment.
In 2020, researchers realized they might use this system for planets orbiting white dwarfs. If such a planet had molecules created by residing organisms in its environment, the James Webb Area Telescope would most likely be capable of spot them when the planet handed in entrance of its star.
In June 2025, I printed a paper answering a query that first began bothering me in 2021: May an ocean – seemingly wanted to maintain life – even survive on a planet orbiting near a lifeless star?
Regardless of its comparatively small measurement, a white dwarf – proven right here as a brilliant dot to the precise of our Solar – is kind of dense.
Kevin Gill/Flickr, CC BY
A universe stuffed with white dwarfs
A white dwarf has about half the mass of the Solar, however that mass is compressed right into a quantity roughly the scale of Earth, with its electrons pressed as shut collectively because the legal guidelines of physics will enable. The Solar has a radius 109 occasions the scale of Earth’s – this measurement distinction signifies that an Earth-like planet orbiting a white dwarf could possibly be about the identical measurement because the star itself.
White dwarfs are extraordinarily widespread: An estimated 10 billion of them exist in our galaxy. And since each low-mass star is destined to finally change into a white dwarf, numerous extra have but to kind. If it seems that life can exist on planets orbiting white dwarfs, these stellar remnants may change into promising and plentiful targets within the seek for life past Earth.
However can life even exist on a planet orbiting a white dwarf? Astronomers have identified since 2011 that the liveable zone is extraordinarily near the white dwarf. This zone is the placement in a planetary system the place liquid water may exist on a planet’s floor. It may possibly’t be too near the star that the water would boil, nor so far-off that it will freeze.
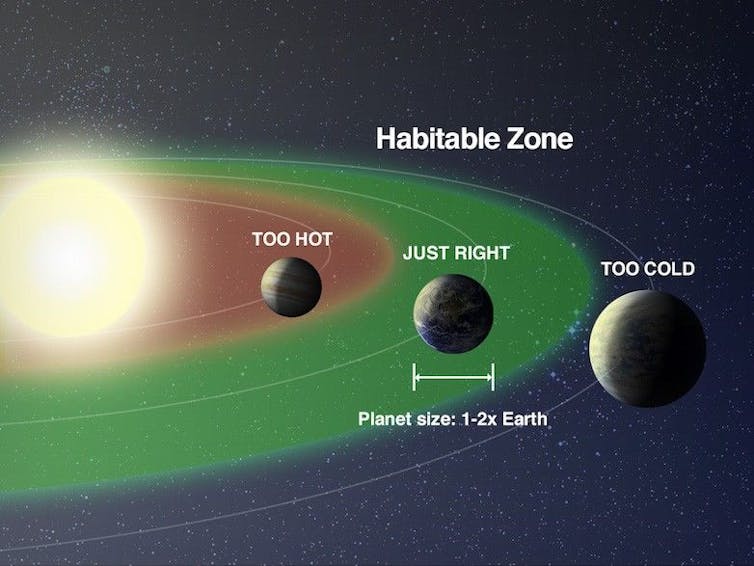
Planets within the liveable zone aren’t so shut that their floor water would boil, but in addition not thus far that it will freeze.
NASA
The liveable zone round a white dwarf can be 10 to 100 occasions nearer to the white dwarf than our personal liveable zone is to our Solar, since white dwarfs are a lot fainter.
The problem of tidal heating
Being so near the floor of the white dwarf would deliver new challenges to rising life that extra distant planets, like Earth, don’t face. Considered one of these is tidal heating.
Tidal forces – the variations in gravitational forces that objects in area exert on completely different elements of a close-by second object – deform a planet, and the friction causes the fabric being deformed to warmth up. An instance of this may be seen on Jupiter’s moon Io.
The forces of gravity exerted by Jupiter’s different moons tug on Io’s orbit, deforming its inside and heating it up, leading to a whole bunch of volcanoes erupting always throughout its floor. Consequently, no floor water can exist on Io as a result of its floor is just too scorching.
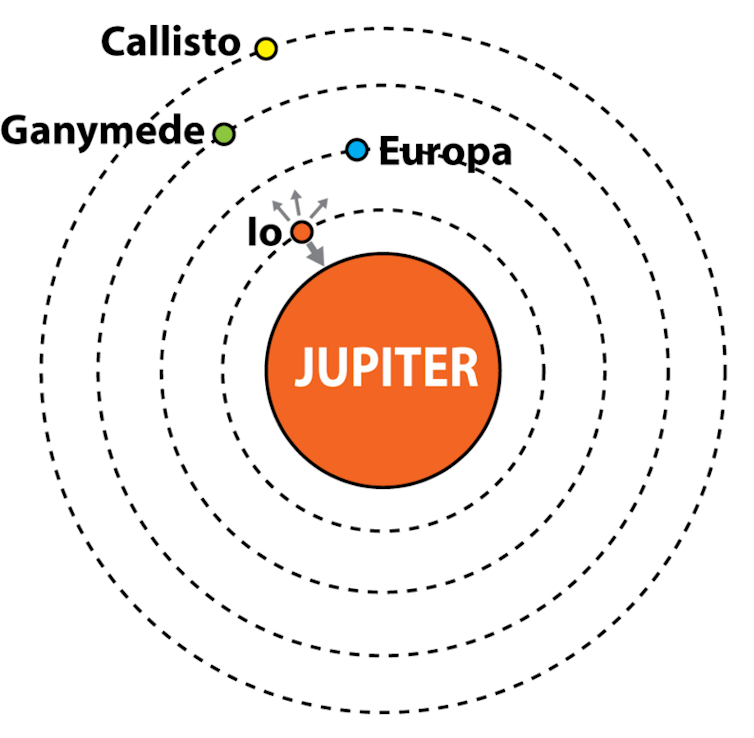
Of the 4 main moons of Jupiter, Io is the innermost one. Gravity from Jupiter and the opposite three moons pulls Io in various instructions, which heats it up.
Lsuanli/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
In distinction, the adjoining moon Europa can be topic to tidal heating, however to a lesser diploma, because it’s farther from Jupiter. The warmth generated from tidal forces has brought on Europa’s ice shell to partially soften, leading to a subsurface ocean.
Planets within the liveable zone of a white dwarf would have orbits shut sufficient to the star to expertise tidal heating, just like how Io and Europa are heated from their proximity to Jupiter.
This proximity itself can pose a problem to habitability. If a system has a couple of planet, tidal forces from close by planets may trigger the planet’s environment to lure warmth till it turns into hotter and warmer, making the planet too scorching to have liquid water.
Enduring the pink big part
Even when there is just one planet within the system, it might not retain its water.
Within the technique of changing into a white dwarf, a star will broaden to 10 to 100 occasions its authentic radius throughout the pink big part. Throughout that point, something inside that expanded radius can be engulfed and destroyed. In our personal photo voltaic system, Mercury, Venus and Earth can be destroyed when the Solar finally turns into a pink big earlier than transitioning right into a white dwarf.
For a planet to outlive this course of, it must begin out a lot farther from the star — maybe on the distance of Jupiter and even past.
If a planet begins out that far-off, it will have to migrate inward after the white dwarf has shaped in an effort to change into liveable. Laptop simulations present that this type of migration is feasible, however the course of may trigger excessive tidal heating that will boil off floor water – just like how tidal heating causes Io’s volcanism. If the migration generates sufficient warmth, then the planet may lose all its floor water by the point it lastly reaches a liveable orbit.
Nevertheless, if the migration happens late sufficient within the white dwarf’s lifetime – after it has cooled and is not a scorching, brilliant, newly shaped white dwarf – then floor water might not evaporate away.
Below the precise circumstances, planets orbiting white dwarfs may maintain liquid water and probably assist life.
Seek for life on planets orbiting white dwarfs
Astronomers haven’t but discovered any Earth-like, liveable exoplanets round white dwarfs. However these planets are troublesome to detect.
Conventional detection strategies just like the transit method are much less efficient as a result of white dwarfs are a lot smaller than typical planet-hosting stars. Within the transit method, astronomers look ahead to the dips in mild that happen when a planet passes in entrance of its host star from our line of sight. As a result of white dwarfs are so small, you would need to be very fortunate to see a planet passing in entrance of 1.
The transit method for detecting exoplanets requires expecting the dip in brightness when a planet passes in entrance of its host star.
Nonetheless, researchers are exploring new methods to detect and characterize these elusive worlds utilizing superior telescopes such because the Webb telescope.
If liveable planets are discovered to exist round white dwarfs, it will considerably broaden the vary of environments the place life would possibly persist, demonstrating that planetary methods might stay viable hosts for all times even lengthy after the dying of their host star.



