Enzymes are molecular machines that perform the chemical reactions that maintain all life, a capability that has captured the eye of scientists like me.
Take into account muscle motion. Your physique releases a molecule referred to as acetylcholine to set off your muscle cells to contract. If acetylcholine sticks round for too lengthy, it will possibly paralyze your muscle mass – together with your coronary heart muscle cells – and, nicely, that’s that. That is the place the enzyme acetylcholinesterase is available in. This enzyme can break down 1000’s of acetylcholine molecules per second to make sure muscle contraction is stopped, paralysis averted and life continued. With out this enzyme, it will take a month for a molecule of acetylcholine to interrupt down by itself – about 10 billion occasions slower.
You’ll be able to think about why enzymes are of specific curiosity to scientists seeking to resolve trendy issues. What if there have been a approach to break down plastic, seize carbon dioxide or destroy most cancers cells as quick as acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine? If the world must take motion rapidly, enzymes are a compelling candidate for the job – if solely researchers may design them to deal with these challenges on demand.
Designing enzymes, sadly, may be very arduous. It’s like working with an atom-sized Lego set, however the directions have been misplaced and the factor gained’t maintain collectively until it’s assembled completely. Newly printed analysis from our crew means that machine studying can act because the architect on this Lego set, serving to scientists construct these advanced molecular constructions precisely.
What’s an enzyme?
Let’s take a better take a look at what makes up an enzyme.
Enzymes are proteins – massive molecules that do the behind-the-scenes work that maintain all residing issues alive. These proteins are made up of amino acids, a set of constructing blocks that may be stitched collectively to type lengthy strings that get tangled up into particular shapes.
The precise construction of a protein is vital to its perform in the identical means that the shapes of on a regular basis objects are. For instance, very similar to a spoon is designed to carry liquid in a means {that a} knife merely can’t, the enzymes concerned in transferring your muscle mass aren’t nicely suited to photosynthesis in vegetation.
For an enzyme to perform, it adopts a form that completely matches the molecule it processes, very similar to a lock matches a key. The distinctive grooves within the enzyme – the lock – that work together with the goal molecule – the important thing – are present in a area of the enzyme often called the energetic web site.
The induced match mannequin of enzymes states that each the enzyme and its substrate change form once they work together.
OpenStax, CC BY-SA
The energetic web site of the enzyme exactly orients amino acids to work together with the goal molecule when it enters. This makes it simpler for the molecule to bear a chemical response to show into a unique one, making the method go sooner. After the chemical response is finished, the brand new molecule is launched and the enzyme is able to course of one other.
How do you design an enzyme?
Scientists have spent many years attempting to design their very own enzymes to make new molecules, supplies or therapeutics. However making enzymes that seem like and go as quick as these present in nature is extremely tough.
Enzymes have advanced, irregular shapes which can be made up of tons of of amino acids. Every of those constructing blocks must be positioned completely or else the enzyme will decelerate or utterly shut off. The distinction between a velocity racer and slowpoke enzyme could be a distance of lower than the width of a single atom.
Initially, scientists targeted on modifying the amino acid sequences of present enzymes to enhance their velocity or stability. Early successes with this method primarily improved the soundness of enzymes, enabling them to catalyze chemical reactions at a better vary of temperatures. However this method was much less helpful for bettering the velocity of enzymes. To today, designing new enzymes by modifying particular person amino acids is mostly not an efficient means to enhance pure enzymes.
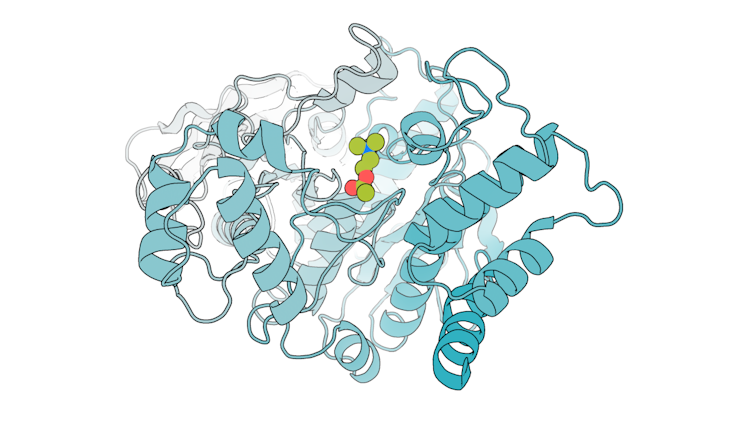
This mannequin of acetylcholinesterase exhibits acetylcholine (inexperienced) certain to its energetic web site.
Sam Pellock, CC BY-SA
Researchers discovered that utilizing a course of referred to as directed evolution, wherein the amino acid sequence of an enzyme is randomly modified till it will possibly carry out a desired perform, proved rather more fruitful. For instance, research have proven that directed evolution can enhance chemical response velocity, thermostability, and even generate enzymes with properties that aren’t seen in nature. Nevertheless, this method is usually labor-intensive: You must display many mutants to seek out one which does what you need. In some circumstances, if there’s no good enzyme to start out from, this technique can fail to work in any respect.
Each of those approaches are restricted by their reliance on pure enzymes. That’s, proscribing your design to the shapes of pure proteins seemingly limits the sorts of chemistry that enzymes can facilitate. Bear in mind, you’ll be able to’t eat soup with a knife.
Is it attainable to make enzymes from scratch, quite than modify nature’s recipe? Sure, with computer systems.
Designing enzymes with computer systems
The primary makes an attempt to computationally design enzymes nonetheless largely relied on pure enzymes as a place to begin, specializing in putting enzyme energetic websites into pure proteins.
This method is akin to looking for a swimsuit at a thrift retailer: It’s unlikely you will see an ideal match as a result of the geometry of an enzyme’s energetic web site (your physique on this analogy) is extremely particular, so a random protein with a rigidly mounted construction (a swimsuit with random measurements) is unlikely to completely accommodate it. The ensuing enzymes from these efforts carried out rather more slowly than these present in nature, requiring additional optimization with directed evolution to succeed in speeds frequent amongst pure enzymes.
Latest advances in deep studying have dramatically modified the panorama of designing enzymes with computer systems. Enzymes can now be generated in a lot the identical means that AI fashions akin to ChatGPT and DALL-E generate textual content or photos, and also you don’t want to make use of native protein constructions to assist your energetic web site.
AI instruments are serving to researchers design new proteins.
Our crew confirmed that after we immediate an AI mannequin, referred to as RFdiffusion, with the construction and amino acid sequence of an energetic web site, it will possibly generate the remainder of the enzyme construction that might completely assist it. That is equal to prompting ChatGPT to put in writing a complete brief story primarily based on a immediate that solely says to incorporate the road “And sadly, the eggs never showed up.”
We used this AI mannequin particularly to generate enzymes referred to as serine hydrolases, a bunch of proteins which have potential functions in drugs and plastic recycling. After designing the enzymes, we combined them with their supposed molecular goal to see whether or not they may catalyze its breakdown. Encouragingly, lots of the designs we examined have been in a position to break down the molecule, and higher than beforehand designed enzymes for a similar response.
To see how correct our computational designs have been, we used a technique referred to as X-ray crystallography to find out the shapes of those enzymes. We discovered that a lot of them have been a virtually excellent match to what we digitally designed.
Our findings mark a key advance in enzyme design, highlighting how AI might help scientists begin to sort out advanced issues. Machine studying instruments may assist extra researchers entry enzyme design and faucet into the total potential of enzymes to resolve modern-day issues.



