For many years, army medical doctors confronted a important problem: What’s the easiest way to soundly and successfully ship oxygen to sufferers in distant fight zones, rural hospitals or disaster-stricken areas?
Oxygen tanks are heavy, pricey and harmful in fight zones. A direct hit from a missile or a bullet can flip a lifesaving useful resource right into a lethal hazard.
Marine Corps Gen. Ernest T. Prepare dinner as soon as stated, “Logistics is the hard part of fighting a war.” It goes past oxygen. For deployed U.S. troops, the provides obtainable throughout fight for treating wounded troopers can imply the distinction between life and demise.
The Division of Protection turned to us, army physicians and tutorial researchers in army drugs on the College of Colorado Middle for COMBAT Analysis, to review whether or not the army must deliver oxygen to the battlefield for troopers – and, in that case, how a lot.
This strategy to analysis is named a military-civilian partnership. These partnerships intention to save lots of lives on the battlefield. However in addition they save lives throughout the U.S. by turning army medical positive factors into higher well being take care of all.
Innovation and agility
Within the civilian world, it takes 17 years on common for a analysis discovery to alter medical follow. One of the well-known examples of that is using tranexamic acid for trauma sufferers. Tranexamic acid is injected to cease bleeding throughout surgical procedure or after trauma. It was found in 1962 however not permitted by the FDA till 1986. It wasn’t used for traumatic bleeding till 2012.
The altering nature of conflict and threats towards U.S. forces require army drugs to maneuver quicker. Accidents and infections in fight push researchers to seek out higher methods to save lots of lives, usually quicker than in civilian well being care.
Army drugs should transfer shortly to maintain up with the tempo of conflict.
Contributor/Anadolu by way of GettyImages
On the heart, scientists work facet by facet with army medical groups to review, develop and check options tailor-made for the battlefield.
Whether or not it’s addressing oxygen use, traumatic mind accidents, burn therapies or trauma care, these partnerships enable army and civilian researchers to translate discoveries into follow quickly.
Rethinking oxygen
The rapid administration of oxygen to an injured or sick affected person has lengthy been a cornerstone of trauma and burn care. The logic appeared easy: When sufferers are in shock or have extreme accidents, their our bodies wrestle to get sufficient oxygen, so medical doctors supplied additional.
Our analysis, and that of others, discovered that an excessive amount of oxygen can really be dangerous. Extra oxygen triggers oxidative stress – an overload of unstable molecules referred to as free radicals that may harm wholesome cells. That may result in extra irritation, slower therapeutic and even organ failure.
In brief, whereas oxygen is important, extra isn’t at all times higher.
We performed a collection of military-civilian collaborative trials referred to as Technique to Keep away from Extreme Oxygen, or SAVE-O2. We found that severely injured sufferers usually require much less oxygen than beforehand believed. In actual fact, little or no supplemental oxygen is required to soundly take care of 95% of those sufferers.
This discovering challenges many years of typical medical knowledge. It can reshape how medical professionals strategy important care in not solely army settings, however civilian hospitals as properly.
Inside a 12 months of presenting our findings to army medical leaders, these insights have already influenced modifications and updates to affected person care pointers, medic coaching and even selections on medical tools purchases.
To construct on our findings, we’ve launched a trial to review using synthetic intelligence to automate oxygen supply. This military-funded research might present higher take care of wounded troopers in distant fight zones and for injured civilians in ambulances or rural hospitals earlier than they attain massive referral and trauma facilities.
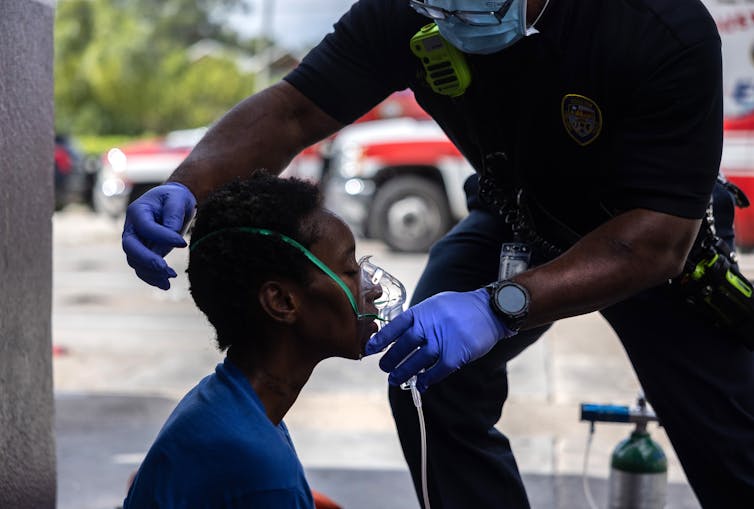
An oxygen masks that makes use of synthetic intelligence might assist medics in rural fight zones and rural U.S. hospitals.
John Moore/GettyImages
In rural or distant areas of the U.S., entry to supplemental oxygen could be restricted attributable to provide chain challenges, excessive prices and shortages. That is significantly true in small hospitals and impacts first responders after a pure catastrophe or accident. Within the intensive care models of those hospitals, utilizing oxygen extra effectively might protect restricted oxygen provides for sufferers who want it.
Extended casualty care: A brand new frontier
Whereas researching oxygen wants in fight zones, we realized one other urgent concern: the challenges of extended casualty care. Throughout a battle, army medics usually must deal with critically injured troopers for hours and even days earlier than the wounded individual could be evacuated.
In a future battle with a “near-peer” adversary corresponding to China or Russia, the U.S. might not have the power to evacuate wounded troops shortly. With out dependable helicopter or airplane transport, many casualties might not attain trauma care throughout the “golden hour.” That is the important first 60 minutes after a extreme harm, when speedy therapy is important.
The continuing conflict in Ukraine illustrates the problem of extended casualty care. In hospitals throughout Ukraine, medical doctors are more and more having bother treating the injuries of civilian and army sufferers due to rising antibiotic resistance.
Future army conflicts within the Indo-Pacific areas will current comparable challenges, together with lengthy affected person transport instances and considerations about wound infections attributable to extended casualty care.
Nevertheless, this problem isn’t distinctive to the battlefield. Extended casualty care additionally occurs in civilian crises. For instance, throughout a pure catastrophe, emergency responders should handle sufferers with out fast entry to hospitals.
As soon as sufferers are handled within the discipline or in catastrophe situations, suppliers should usually maintain care with restricted assets. They need to prioritize important interventions, reduce useful resource use and stabilize sufferers for eventual switch to increased ranges of care.
Innovation in well being care thrives on collaboration. Army-civilian partnerships are one option to advance medical options quicker and extra successfully. These improvements save lives in fight, enhance care and permit us to use our 98% survival price in conflict to our trauma facilities, rural hospitals and catastrophe zones within the U.S.



