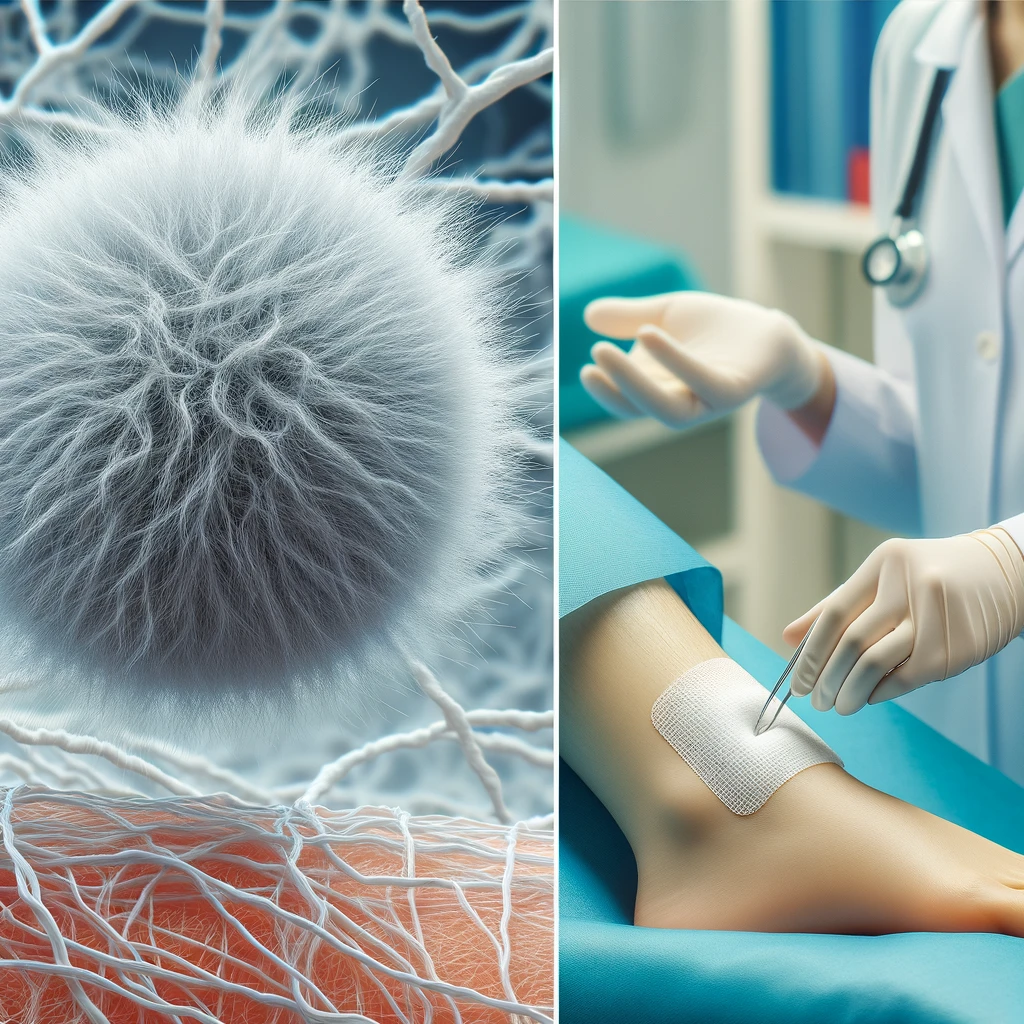
In a landmark advancement, Dipasree Bhowmick and her team have introduced revolutionary nanofiber technology poised to redefine medical care and diagnostics across the United States. This innovation has the potential to not only enhance patient healing but also to provide significant economic relief in a sector where costs are expected to burgeon to $18.7 billion by 2027 in the United States alone.
In a nation where chronic wounds affect 6.5 million individuals, with up to 2% of Americans likely to experience a chronic wound during their lives, the impact of this innovation cannot be overstated. Traditional wound care, with its frequent changes and long treatment periods, places a hefty financial strain on both patients and healthcare systems due to the increased cost of materials and extended hospital stays. Nanofiber dressings, on the other hand, are highly efficient due to their ability to closely mimic the natural structure of human tissue, promote rapid cell growth, and maintain an optimal healing environment. This can lead to reduced hospital stays and a decrease in the overall treatment costs, thereby alleviating the financial burden on both patients and healthcare systems. Recent surveys highlight that while traditional dressings need changing every 2 to 4 days, nanofiber dressings excel with changes required only every 7 days or more, underscoring their enhanced durability and the potential to diminish wound care frequency.
The financial implications of wound care are substantial, with the U.S. spending $3.5 billion in 2021 and an alarming escalation projected in the coming years. The social impact is equally significant, with chronic wounds contributing to an 11% job loss rate among those affected, the quick and effective healing properties of nanofibers can significantly reduce the recovery period, enabling patients to return to work sooner and avoid the spiral into disability or early retirement. Bhowmick’s nanofiber technology addresses these issues head-on by facilitating faster wound healing, potentially reducing the time individuals spend away from work and lowering the risk of long-term disability.

Environmentally, innovation marks a positive shift. With 23% of medical waste attributed to traditional wound dressings and a predicted increase by 31% by 2050, the adoption of Bhowmick’s efficient nanofiber dressings can considerably decrease waste. These new dressings, closely resembling human tissue structure, promote cell growth and maintain a moist healing environment, key factors in rapid recovery. Their high absorption rate and large surface area for delivering vital bioactive ingredients, such as drugs and growth factors, can significantly decrease the material needed per treatment, further lessening the environmental footprint.
Economically, the benefits are multifaceted. A more efficient healing process reduces the cost burden on healthcare systems by shortening hospital stays and minimizing the need for additional treatments. With a projected $15 billion global market for wound closure by 2022, the United States stands to gain a competitive edge in this expanding field. This innovation could contribute to reducing the national healthcare expenditure while simultaneously bolstering the bio-tech sector’s growth and employment.
. Dipasree Bhowmick, a recent graduate of University of Texas Rio Grande Valley (UTRGV), with a master’s in mechanical engineering, stands at the vanguard of this healthcare revolution. Her research, therefore, represents more than just a medical advancement; it is a step towards a sustainable, economically viable, and environmentally conscious healthcare practice. In the face of rising healthcare demands, her team’s work offers a solution that benefits patients, healthcare providers, and the planet. An international student hailing from Bangladesh, her passion for innovation is matched by a commitment to sustainability—a principle she embodied as a research fellow at UTRGV. Her aim is to craft technological solutions that enhance global health while also nurturing an environmentally sustainable approach within the healthcare sector.
You may also like
-
Bills co-owner Kim Pegula escorted on field in latest sign of her recovery from cardiac arrest
-
How to Get a Digital Nomad Visa in Thailand: Global Mobility Institute
-
Abortion-rights extremists to apologize, pay restitution for attacks on pro-life facilities
-
Biden's virus symptoms are gone, says his doctor
-
A Cockney Rosebud: New Bittersweet and Poignant Memoir Captivates with Tale of Early 20th Century East End Family Life