When Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun found a brand new molecule they known as microRNA within the Eighties, it was a captivating diversion from what for many years had been known as the central dogma of molecular biology.
Acknowledged with the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or drugs, Ambros and Ruvkun had recognized a brand new sort of genetic materials that remodeled how researchers understood gene regulation.
Like DNA, RNA is a type of genetic materials constructed from particular person nucleotides linked into chains. In line with the central dogma, genetic data flows in a single route: DNA is transcribed into RNA, and RNA is translated into proteins. However in a single main deviation from the central dogma, some RNAs are by no means translated or coded into proteins.
MicroRNA is one kind of those so-called noncoding RNAs. They’re quick stretches of genetic materials that, somewhat than coding for a particular protein themselves, management the RNAs that do code for proteins. In impact, microRNAs flip specific genes on and off.
I devoted my scientific profession to understanding how RNA works, partially as a result of analysis on RNA has lagged behind different macromolecules like DNA and proteins. The Nobel Prize recognition of microRNA molecules marks each their significance in biology and their promise as potential therapies for varied ailments, together with most cancers.
MicroRNAs play a key function in regulating gene expression.
MicroRNAs and illness
Scientists regard microRNAs as grasp regulators of the genome as a result of their capability to bind to and alter the expression of many protein-coding RNAs. Certainly, a single microRNA can regulate anyplace from 10 to 100 protein-coding RNAs. Reasonably than translating DNA to proteins, they as a substitute can bind to protein-coding RNAs to silence genes.
The explanation microRNAs can regulate such a various pool of RNAs stems from their capability to bind to focus on RNAs they don’t completely match up with. This implies a single microRNA can usually regulate a pool of targets which might be all concerned in related processes within the cell, resulting in an enhanced response.
As a result of a single microRNA can regulate a number of genes, many microRNAs can contribute to illness once they change into dysfunctional.
In 2002, researchers first recognized the function dysfunctional microRNAs play in illness by way of sufferers with a kind of blood and bone marrow most cancers known as power lymphocytic leukemia. This most cancers outcomes from the lack of two microRNAs usually concerned in blocking tumor cell progress. Since then, scientists have recognized over 2,000 microRNAs in folks, a lot of that are altered in varied ailments.
The sector has developed a reasonably stable understanding of how microRNA dysfunction contributes to illness. Altering one microRNA can change a number of different genes, leading to a plethora of alterations that may collectively reshape the cell’s physiology. For instance, over half of all cancers have considerably lowered exercise in a microRNA known as miR-34a. As a result of miR-34a regulates many genes concerned in stopping the expansion and migration of most cancers cells, shedding miR-34a can enhance the chance of growing most cancers.
Researchers are trying into utilizing microRNAs as therapeutics for most cancers, coronary heart illness, neurodegenerative illness and others. Whereas ends in the laboratory have been promising, bringing microRNA therapies into the clinic has met a number of challenges. Many are associated to inefficient supply into goal cells and poor stability, which restrict their effectiveness.
MicroRNA can silence genes by binding to mRNA.
Kajsa Mollersen/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Delivering microRNA to cells
One cause why delivering microRNA therapies into cells is tough is as a result of microRNA therapies have to be delivered particularly to diseased cells whereas avoiding wholesome cells. Not like mRNA COVID-19 vaccines which might be taken up by scavenging immune cells whose job is to detect international supplies, microRNA therapies have to idiot the physique into considering they aren’t international with a purpose to keep away from immune assault and get to their meant cells.
Scientists are finding out varied methods to ship microRNA therapies to their particular goal cells. One methodology garnering an excessive amount of consideration depends on straight linking the microRNA to a ligand, a sort of small molecule that binds to particular proteins on the floor of cells. In contrast with wholesome cells, diseased cells can have a disproportionate variety of some floor proteins, or receptors. So, ligands may help microRNAs house particularly to diseased cells whereas avoiding wholesome cells. The primary ligand authorised by the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration to ship small RNAs like microRNAs, N-acetylgalactosamine, or GalNAc, preferentially delivers RNAs to liver cells.
Figuring out ligands that may ship small RNAs to different cells requires discovering receptors expressed at excessive sufficient ranges on the floor of goal cells. Usually, over a million copies per cell are wanted with a purpose to obtain ample supply of the drug.
One ligand that stands out is folate, additionally known as vitamin B9, a small molecule crucial in periods of fast cell progress similar to fetal growth. As a result of some tumor cells have over a million folate receptors, this ligand offers ample alternative to ship sufficient of a therapeutic RNA to focus on several types of most cancers. For instance, my laboratory developed a brand new molecule known as FolamiR-34a – folate linked to miR-34a – that lowered the dimensions of breast and lung most cancers tumors in mice.
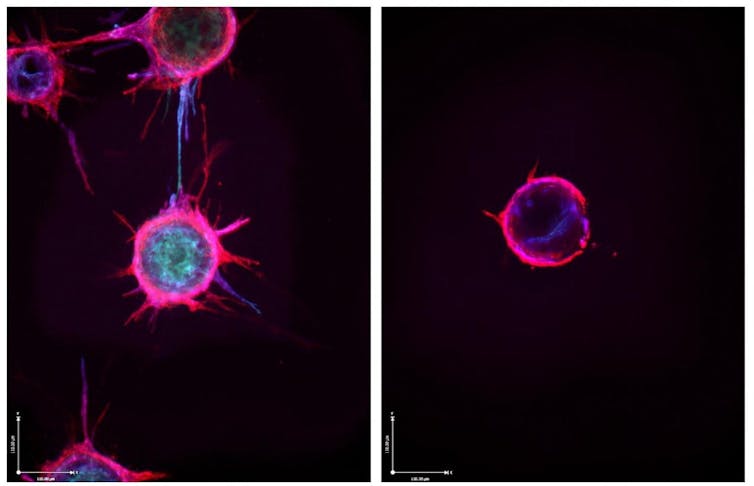
Tumors can exploit wholesome cells to develop blood vessels that present them vitamins, as seen within the endothelial cells to the left sprouting extensions. Exposing these cells to sure microRNAs, nonetheless, can disable that progress, as seen within the cell to the appropriate.
Dudley Lab, College of Virginia Faculty of Drugs/NIH by way of Flickr, CC BY-NC
Making microRNAs extra steady
One of many different challenges with utilizing small RNAs is their poor stability, which results in their fast degradation. As such, RNA-based therapies are usually short-lived within the physique and require frequent doses to keep up a therapeutic impact.
To beat this problem, researchers are modifying small RNAs in varied methods. Whereas every RNA requires a particular modification sample, profitable adjustments can considerably enhance their stability. This reduces the necessity for frequent dosing, subsequently reducing remedy burden and price.
For instance, modified GalNAc-siRNAs, one other type of small RNAs, reduces dosing from each few days to as soon as each six months in nondividing cells. My group developed folate ligands linked to modified microRNAs for most cancers remedy that lowered dosing from as soon as each different day to as soon as per week. For ailments like most cancers the place cells are quickly dividing and shortly diluting the delivered microRNA, this enhance in exercise is a major development within the area. We anticipate this accomplishment will facilitate additional growth of this folate-linked microRNA as a most cancers remedy within the years to return.
Many labs are working to develop therapies based mostly on the discoveries new Nobel laureates Ambros and Ruvkun made many years in the past. Whereas there’s nonetheless appreciable work to be executed to beat the hurdles related to microRNA therapies, it’s clear that RNA reveals promise as a therapeutic for a lot of ailments.
That is an up to date model of an article initially revealed on Nov. 29, 2023.



