Off the coast of Baja California in December 2022, solar sparkled over the rippling sea as waves sloshed across the USS Portland dock ship. Navy officers on the deck scrutinized the sky in the hunt for an indication. The glow appeared all of a sudden.
A tiny spot at first, it progressively grew to a spherical circle falling at an incredible velocity from the fringes of area. It was NASA’s Orion capsule, which might quickly finish the 25-day Artemis I mission round and past the Moon with a fiery splashdown into the ocean.
Orion’s reentry adopted a sharply angled trajectory, throughout which the capsule fell at an unimaginable velocity earlier than deploying three crimson and white parachutes. Because the mission completed its journey of over 270,000 miles (435,000 kilometers), it regarded to these on the deck of the USS Portland just like the capsule had made it residence in a single piece.
Because the restoration crew lifted Orion to the service’s deck, shock waves ruffled throughout the capsule’s floor. That’s when crew members began to identify large cracks on Orion’s decrease floor, the place the capsule’s exterior bonds to its warmth protect.
The Orion spacecraft splashed down in December 2022, marking the top of the Artemis I mission.
However why wouldn’t a protect that has endured temperatures of about 5,000 levels Fahrenheit (2,760 levels Celsius) maintain injury? Appears solely pure, proper?
This mission, Artemis I, was uncrewed. However NASA’s final goal is to ship people to the Moon in 2026. So, NASA wanted to make it possible for any injury to the capsule– even its warmth protect, which is supposed to take some injury – wouldn’t threat the lives of a future crew.
On Dec. 11, 2022 – the time of the Artemis I reentry – this protect took extreme injury, which delayed the following two Artemis missions. Whereas engineers at the moment are working to stop the identical points from taking place once more, the brand new launch date targets April 2026, and it’s developing quick.
As a professor of aerospace know-how, I take pleasure in researching how objects work together with the ambiance. Artemis I provides one notably attention-grabbing case – and an argument for why having a useful warmth protect is crucial to an area exploration mission.
NASA’s Orion spacecraft had a view of each Earth and the Moon through the Artemis I mission.
NASA by way of AP
Taking the warmth
To know what precisely occurred to Orion, let’s rewind the story. Because the capsule reentered Earth’s ambiance, it began skimming its larger layers, which acts a bit like a trampoline and absorbs a part of the approaching spacecraft’s kinetic vitality. This maneuver was fastidiously designed to progressively lower Orion’s velocity and scale back the warmth stress on the interior layers of the protect.
After the primary dive, Orion bounced again into area in a calculated maneuver, dropping a few of its vitality earlier than diving once more. This second dive would take it to decrease layers with denser air because it neared the ocean, reducing its velocity much more.
Whereas falling, the drag from the pressure of the air particles towards the capsule helped decreased its velocity from about 27,000 miles per hour (43,000 kilometers per hour) right down to about 20 mph (32 kph). However this slowdown got here at a price – the friction of the air was so nice that temperatures on the underside floor of the capsule going through the airflow reached 5,000 levels Fahrenheit (2,760 levels Celsius).
At these scorching temperatures, the air molecules began splitting and a sizzling mix of charged particles, known as plasma, fashioned. This plasma radiated vitality, which you can see as crimson and yellow infected air surrounding the entrance of the car, wrapping round it backward within the form of a candle.
No materials on Earth can stand this hellish setting with out being significantly broken. So, the engineers behind these capsules designed a layer of fabric known as a warmth protect to be sacrificed by means of melting and evaporation, thus saving the compartment that will finally home astronauts.
By defending anybody who may sooner or later be contained in the capsule, the warmth protect is a crucial element.
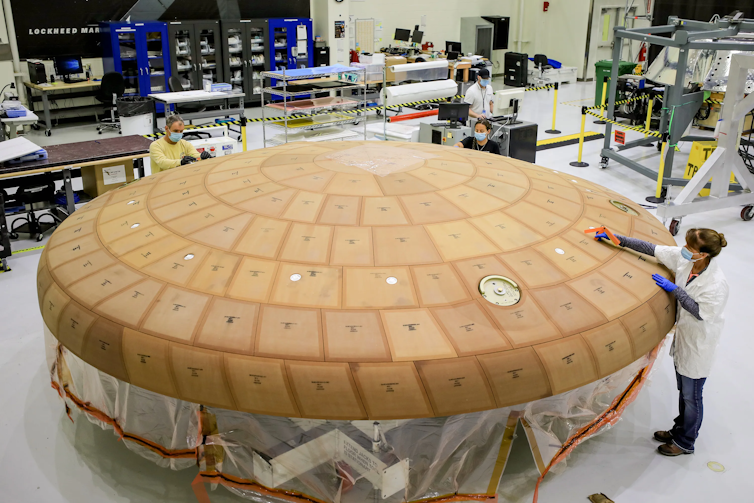

The Orion warmth protect is roofed in tiles made from a cloth that may expend when uncovered to excessive warmth.
NASA/Isaac Watson
Within the type of a shell, it’s this protect that encapsulates the vast finish of the spacecraft, going through the incoming airflow – the most well liked a part of the car. It’s made from a cloth that’s designed to evaporate and take in the vitality produced by the friction of the air towards the car.
The case of Orion
However what actually occurred with Orion’s warmth protect throughout that 2022 descent?
Within the case of Orion, the warmth protect materials is a composite of a resin known as Novolac – a relative to the Bakelite which some firearms are made from – absorbed in a honeycomb construction of fiberglass threads.
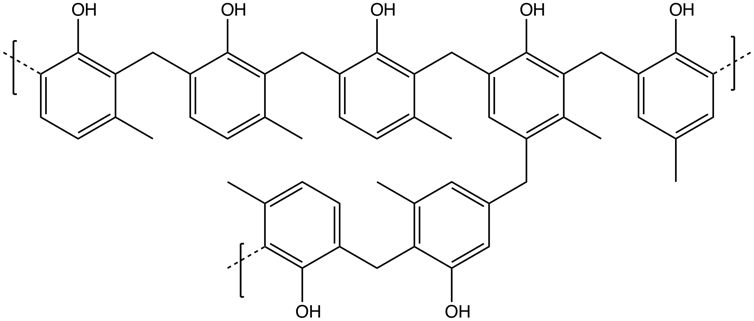
Novolac, the fabric that makes up Orion’s warmth protect, is made up of atoms organized in linked hexagons.
Smokefoot/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Because the floor is uncovered to the warmth and airflow, the resin melts and recedes, exposing the fiberglass. The fiberglass reacts with the encircling sizzling air, producing a black construction known as char. This char then acts as a second warmth barrier.
NASA used the identical warmth protect design for Orion because the Apollo capsule. However through the Apollo missions, the char construction didn’t break prefer it did on Orion.
After practically two years spent analyzing samples of the charred materials, NASA concluded that the Orion undertaking group had overestimated the warmth circulate because the craft skimmed the ambiance upon reentry.
As Orion approached the higher layers of the ambiance, the protect began melting and produced gases that will have escaped by means of pores within the materials. Then, when the capsule gained altitude once more, the outer layers of the resin froze, trapping the warmth from the primary dive inside. This warmth vaporized the resin.
When the capsule dipped into the ambiance the second time, the gasoline expanded earlier than discovering a method out because it heated once more – type of like how a frozen lake thaws upward from the underside – and its escape produced cracks within the capsule’s floor the place the char construction obtained broken. These have been the cracks the restoration crew noticed on the capsule after it splashed down.
In a Dec. 5, 2024, press convention, NASA officers introduced that the Artemis II mission can be designed with a modified reentry trajectory to stop warmth from accumulating.
For Artemis III, which is deliberate to launch in 2027, NASA intends to make use of new manufacturing strategies for the protect, making it extra permeable. The surface of the capsule will nonetheless get highly regarded throughout reentry, and the warmth protect will nonetheless evaporate. However these new strategies will assist preserve the astronauts cozy within the capsule throughout splashdown.
Chonglin Zhang, assistant professor of mechanical engineering on the College of North Dakota, assisted in researching this text.



