A physicist, a chemist and a mathematician stroll right into a bar. It appears like the beginning of a nasty joke, however in my case, it was the beginning of an thought that would reshape how scientists take into consideration the historical past of the Moon.
The three of us have been all within the Moon, however from totally different views: As a geophysicist, I considered its inside; Thorsten Kleine studied its chemistry; and Alessandro Morbidelli needed to know what the Moon’s formation may inform us about how the planets have been assembled 4.5 billion years in the past.
After we acquired collectively to debate how previous the Moon actually was, having these a number of views turned out to be essential.
How did the Moon type?
At a convention in Hawaii within the late Eighties, a gaggle of scientists solved the issue of how the Moon fashioned. Their analysis urged {that a} Mars-size object crashed into the early Earth, jettisoning molten materials into house. That glowing materials coalesced into the physique now known as the Moon.
This story defined many issues. For one, the Moon has little or no materials that evaporates simply, resembling water, as a result of it started life molten. It has solely a tiny iron core, as a result of it was principally fashioned from the outer a part of the Earth, which has little or no iron. And it has a buoyant, white-colored crust made out of minerals that floated to the floor because the molten Moon solidified.
The glowing, newly fashioned Moon was initially very near the Earth, at roughly the space that TV satellites orbit. The early Moon would have raised gigantic tides on the early Earth, which itself was principally molten and spinning quickly.
These tides took power from the Earth’s spin and transferred some to the Moon’s orbit, slowly pushing the Moon away from the Earth and slowing the Earth’s spin as they did so. This movement continues as we speak – the Moon nonetheless recedes from the Earth about 2 inches per 12 months.
An artist’s impression of what the Moon regarded like through the tidal heating occasion. There would have been intense volcanism in every single place. The early Earth would have loomed a lot bigger within the sky as a result of it was nearer.
MPS/Alexey Chizhik
Because the Moon moved away, it handed via specific factors the place its orbit quickly turned disturbed. These orbital disturbances have been an vital part of its historical past and are a key a part of our speculation.
When did the Moon type?
When the Moon really fashioned and receded away from the Earth is a thorny subject.
Due to the Apollo astronauts, scientists have a set of Moon rocks, which they’ll measure the age of. The oldest rocks are all about 4.35 billion years previous, which is roughly 200 million years after the beginning of the photo voltaic system.
Many geochemists, like my colleague Thorsten Kleine, urged (not unreasonably) that the age of those rocks is identical because the age of the Moon.
However folks like Alessandro Morbidelli, who examine planet formation, didn’t like this reply very a lot. Of their fashions, planets swept up many of the materials floating across the early photo voltaic system lengthy earlier than 200 million years had elapsed. A large, Moon-forming impression as late because the rock samples urged appeared fairly unlikely.
What did we propose?
That is the place Kleine, Morbidelli and I got here in. We adopted up on a suggestion from a 2016 examine that discovered the Moon may often expertise excessive heating occasions throughout its sluggish outward journey from Earth.
This heating occurs the identical manner that heating does on Jupiter’s hyperactively volcanic moon Io. The smaller physique’s form will get squeezed and stretched by tides from the large physique. And identical to a rubber ball warms up in the event you squeeze it sufficient, so too do the rocks on Io and the Moon.
All rocks comprise little inside clocks – radioactive parts that decay and permit researchers to inform how previous the rock is. However right here’s the important thing level: If the Moon warmed up sufficient, its clocks would lose their reminiscence and would begin recording time solely as soon as the Moon cooled down once more.
So on this image, the pileup of rocks aged round 4.35 billion years isn’t telling us when the Moon fashioned, however simply when it went via this tidal heating occasion. Which means the Moon’s formation should have occurred earlier.
An early formation date satisfies the physicists learning planet formation, whereas explaining that the later relationship recorded from the rocks is as a result of tidal reheating.
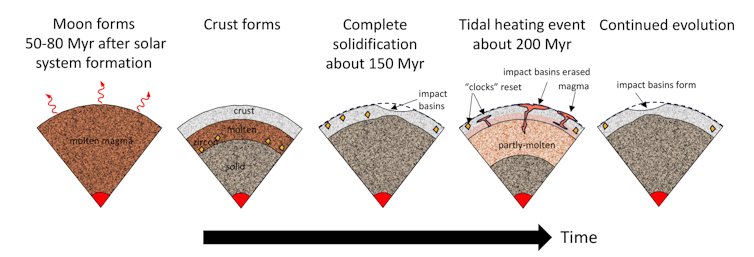
The Moon began out molten after which cooled down, solely to be reheated roughly 100 million years later. This heating occasion may have reset many of the ages recorded by lunar rocks.
Francis Nimmo
What subsequent?
As usually occurs in science, two teams concurrently got here up with an identical thought. Our group targeted on a tidal heating occasion that occurred when the Moon was fairly distant from the Earth, whereas analysis from Steve Desch at Arizona State College factors to an occasion that occurred when the Moon was nearer. Finding out which of those two hypotheses is correct will take a while – and perhaps neither is appropriate.
Testing these hypotheses would require extra samples from the Moon. Fortuitously, China’s Chang’e 6 mission simply returned samples from the darkish facet of the Moon in June 2024. If these samples additionally present plenty of rocks all having ages of round 4.35 billion years in the past, that might be per our story. If the ages are a lot older, we’ll have to determine a brand new story.
Fairly often in earth and planetary sciences, geochemists and geophysicists find yourself with totally different and contradictory hypotheses. This occurs partly as a result of these fields use totally different sorts of measurements, but in addition as a result of they converse very totally different scientific languages. Overcoming this language barrier is tough.
Our examine is an instance of how – typically – bridging that linguistic and scientific divide can profit researchers on each side.



