Microplastics – the tiny particles of plastic shed when litter breaks down – are all over the place, from the deep sea to Mount Everest, and plenty of researchers fear that they might hurt human well being.
I’m a machine studying researcher. With a group of scientists, I’ve developed a software to make identification of microplastics utilizing their distinctive chemical fingerprint extra dependable. We hope that this work will assist us be taught in regards to the kinds of microplastics floating via the air in our examine space, Michigan.
Microplastics – a worldwide drawback
The time period plastic refers to all kinds of artificially created polymers. Polyethylene, or PET, is used for making bottles; polypropylene, or PP, is utilized in meals containers; and polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is utilized in pipes and tubes.
Microplastics are small plastic particles that vary in dimension from 1 micrometer to five millimeters. The width of a human hair, for comparability, ranges from 20 to 200 micrometers.
Most scientific research give attention to microplastics in water. Nonetheless, microplastics are additionally discovered within the air. Scientists know a lot much less about microplastics within the ambiance.
When scientists accumulate samples from the atmosphere to review microplastics, they often wish to know extra in regards to the chemical identities of the microplastic particles discovered within the samples.
Plastic bottles are sometimes product of polyethylene, whereas meals containers often containe polypropylene.
Anton Petrus/Second through Getty Pictures
Fingerprinting microplastics
Simply as fingerprinting uniquely identifies an individual, scientists use spectroscopy to find out the chemical id of microplastics. In spectroscopy, a substance both absorbs or scatters gentle, relying on how its molecules vibrate. The absorbed or scattered gentle creates a novel sample referred to as the spectrum, which is successfully the substance’s fingerprint.
Spectroscopy can match a substance with its distinctive fingerprint.
VectorMine/iStock through Getty Pictures Plus
Similar to a forensic analyst can match an unknown fingerprint towards a fingerprint database to determine the individual, researchers can match the spectrum of an unknown microplastic particle towards a database of identified spectra.
Nonetheless, forensic analysts can get false matches in fingerprint matching. Equally, spectral matching towards a database isn’t foolproof. Many plastic polymers have comparable buildings, so two totally different polymers can have comparable spectra. This overlap can result in ambiguity within the identification course of.
So, an identification technique for polymers ought to present a measure of uncertainty in its output. That means, the person can understand how a lot to belief the polymer fingerprint match. Sadly, present strategies don’t often present an uncertainty measure.
Information from microplastic analyses can inform well being suggestions and coverage selections, so it’s essential for the individuals making these calls to understand how dependable the evaluation is.
Conformal prediction
Machine studying is one software researchers have began utilizing for microplastic identification.
First, researchers accumulate a big dataset of spectra whose identities are identified. Then, they use this dataset to coach a machine studying algorithm that learns to foretell a substance’s chemical id from its spectrum.
Refined algorithms whose interior workings might be opaque make these predictions, so the shortage of an uncertainty measure turns into an excellent larger drawback when machine studying is concerned.
Our current work addresses this concern by making a software with an uncertainty quantification for microplastic identification. We use a machine studying approach referred to as conformal prediction.
Conformal prediction is sort of a wrapper round an present, already educated machine studying algorithm that provides an uncertainty quantification. It doesn’t require the person of the machine studying algorithm to have any detailed information of the algorithm or its coaching knowledge. The person simply wants to have the ability to run the prediction algorithm on a brand new set of spectra.
To arrange conformal prediction, researchers accumulate a calibration set containing spectra and their true identities. The calibration set is commonly a lot smaller than the coaching knowledge required for coaching machine studying algorithms. Often only a few hundred spectra are sufficient for calibration.
Then, conformal prediction analyzes the discrepancies between the predictions and proper solutions within the calibration set. Utilizing this evaluation, it provides different believable identities to the algorithm’s single output on a selected particle’s spectrum. As a substitute of outputting one, presumably incorrect, prediction like “this particle is polyethylene,” it now outputs a set of predictions – for instance, “this particle could be polyethylene or polypropylene.”
The prediction units comprise the true id with a stage of confidence that customers can set themselves – say, 90%. Customers can then rerun the conformal prediction with the next confidence – say, 95%. However the larger the boldness stage, the extra polymer predictions given by the mannequin within the output.
It might sound {that a} technique that outputs a set somewhat than a single id isn’t as helpful. However the dimension of the set serves as a option to assess uncertainty – a small set signifies much less uncertainty.
Alternatively, if the algorithm predicts that the pattern may very well be many various polymers, there’s substantial uncertainty. On this case, you would herald a human knowledgeable to look at the polymer intently.
Testing the software
To run our conformal prediction, my group used libraries of microplastic spectra from the Rochman Lab on the College of Toronto because the calibration set.
As soon as calibrated, we collected samples from a parking zone in Brighton, Michigan, obtained their spectra, and ran them via the algorithm. We additionally requested an knowledgeable to manually label the spectra with the right polymer identities. We discovered that conformal prediction did produce units that included the label the human knowledgeable gave it.
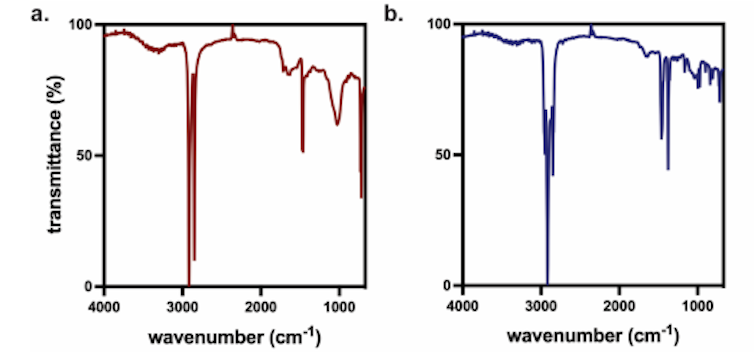
Some spectra, similar to polyethylene on the left and polypropylene on the best, look very comparable and may simply be confused. That’s why having an uncertainty measure might be useful.
Ambuj Tewari
Microplastics are an rising concern worldwide. Some locations similar to California have begun to collect proof for future laws to assist curb microplastic air pollution.
Proof-based science will help researchers and policymakers totally perceive the extent of microplastic air pollution and the threats it poses to human welfare. Constructing and brazenly sharing machine learning-based instruments is a technique to assist make that occur.



