It in all probability feels apparent that having an in depth pal can affect your well-being. However do the teams that you just’re part of additionally have an effect on your well-being? For instance, does the tradition of your work colleagues affect your productiveness?
It could appear to be the reply can be an apparent “yes.” However the concept a bunch’s composition or construction can have an effect on the people in it has been among the many most controversial concepts in biology.
This phenomenon, referred to as multilevel choice, is an extension of pure choice: the method by which organisms with traits higher suited to their setting usually tend to survive and reproduce. Over generations, these advantageous traits – behavioral, morphological or physiological – grow to be extra widespread within the inhabitants.
Within the conventional view of how evolution works, pure choice acts on a person organism’s traits. As an example, mammals with extra buddies usually stay longer lives and have extra offspring. The trait underneath choice on this case is the variety of social connections.
Multilevel choice proposes that on the similar time choice is going on on the traits of people, choice additionally acts on the traits of teams. Right here’s an instance: Dwelling in a extra social and interconnected group could also be helpful for the members of that group, which means the group’s traits are underneath choice. In nature, this implies people in well-connected teams might stay longer lives and have extra offspring as a result of well-connected teams could also be higher at discovering restricted sources or detecting predators. The traits of the group as a complete are what’s underneath choice on this case.
Multilevel choice might even choose for traits that appear at odds on the particular person and group ranges. As an example, it might imply that choice favors people which are extra reserved whereas on the similar time favoring teams which are very social, or vice versa.
Multilevel choice has been a controversial concept since Charles Darwin first instructed that teams doubtless have an effect on people in his 1871 e book “The Descent of Man.”
The one proof for multilevel choice appearing concurrently on people’ social relationships and on social teams comes from laboratory experiments. Experiments like these are important to the scientific course of, however with out proof for multilevel choice in wild animals, the 154-year-old debate rages on. As two area biologists within the evolution of habits, we investigated multilevel choice within the wild by learning yellow-bellied marmots.
Our newly revealed research supplies help for this contested idea, suggesting that the construction of the teams marmots are members of might matter for survival simply as a lot as, if no more than, the pleasant one-on-one relationships they’ve with different marmots.
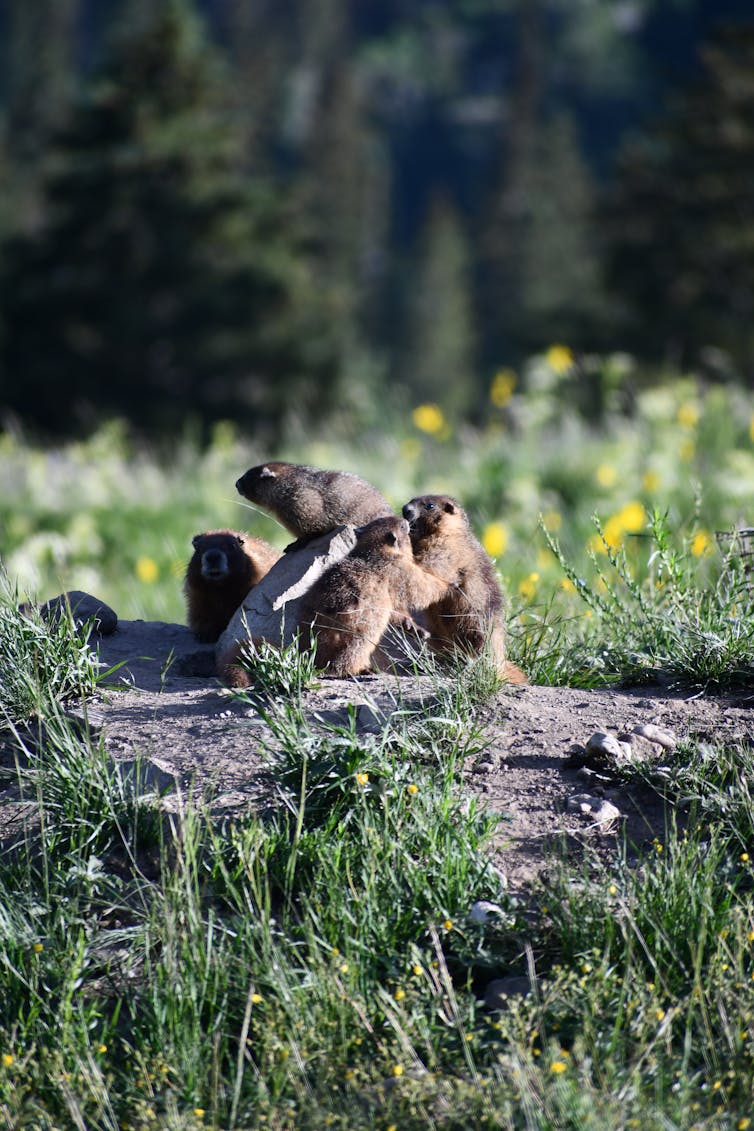
Conner Philson observing the marmots’ social habits.
G. Johnson
Spying on marmots’ social lives
It’s taken a century and a half to reply the query of multilevel choice since you want an unimaginable quantity of information to have an enough pattern measurement to deal with it.
Scientists on the Rocky Mountain Organic Laboratory in Crested Butte, Colorado, have been learning the marmots close by since 1962. This analysis is the second-longest research of individually identifiable wild mammals on the earth.
Annually, the group ensures that every one marmots are individually marked. We lure them so we can provide them distinctive ear tags and paint a mark on their again that lets us determine them from afar. Then skilled “marmoteers,” as we name them, spend about 1,000 hours a yr watching these chunky cat-sized rodents by means of binoculars and recognizing scopes.
Since 2003, the group has paid explicit consideration to the marmots’ social interactions and relationships. Our evaluation of multilevel choice was based mostly on 42,369 distinctive affiliative social interactions – behaviors comparable to taking part in and grooming – between 1,294 people from 180 social teams, with group sizes starting from two to 35 marmots. We additionally tracked how lengthy marmots lived – as much as 16 years in some instances – and what number of offspring particular person animals had annually.
Utilizing this knowledge, we mapped out the marmots’ social networks. Our purpose was to determine what number of social relationships every marmot had, who was linked to whom, and the general construction of every group.
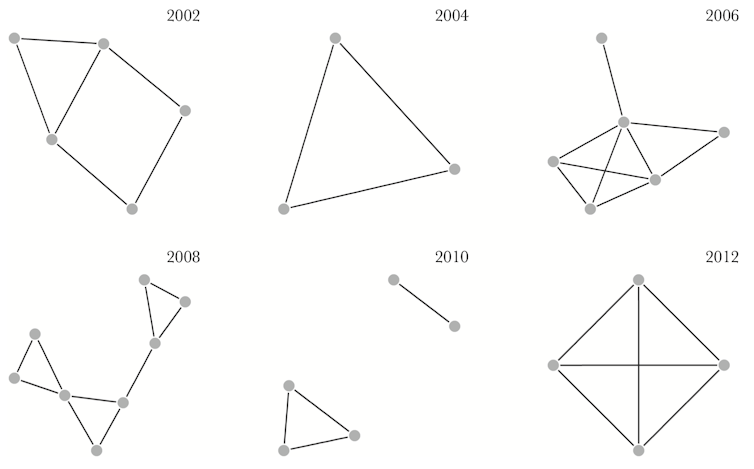
From yr to yr, marmots fashioned totally different small social networks, connecting with varied different people.
Maldonado-Chaparro et al, Behavioral Ecology, 2015.
Understanding all these marmot connections allow us to ask two essential questions. First, how do social relationships have an effect on particular person survival and copy – that’s, what particular person traits are underneath choice? Second, how do social teams have an effect on particular person survival and copy – in different phrases, what group traits are underneath choice?
Importantly, we didn’t ask these two questions in isolation – we requested them on the similar time. In spite of everything, marmots are influenced concurrently by each their social relationships and the social teams they’re a part of. Our statistical method, which researchers name contextual evaluation, tells us how a lot social relationships and social teams matter relative to one another.
New proof adjustments the talk
It may be difficult to differentiate how group-level choice differs from conventional individual-level choice. It’s like a extra complicated model of eager about the relationships that have an effect on a person. As an alternative of simply your individual habits affecting you, your group – a product of many people – is affecting you.
Our new evaluation exhibits that there’s certainly multilevel choice for social habits within the wild. We discovered that not solely do each social relationships and social teams have an effect on particular person animals’ survival and copy, however social teams matter simply as a lot, if no more. We calculated the choice gradient, a measure of how robust the choice is on a trait, to be 0.76 for particular person traits, whereas for group traits it was 1.03.
4 juvenile yellow-bellied marmots play collectively.
D.T. Blumstein
Apparently, the kind of impression on survival and copy wasn’t at all times the identical throughout the 2 ranges. In some instances, choice favored marmots with fewer social relationships whereas favoring marmots residing in additional social and linked teams. In human phrases, consider an introvert at a extremely bustling social gathering.
Evolution and multilevel choice are complicated pure processes, so a lot of these difficult findings usually are not surprising.
Multilevel choice is related for human teams, too, which are available in many varieties, whether or not pal teams, native communities, companies we frequent or work at, economies and even whole nations. Our marmot research suggests it’s not uniquely human for teams at each stage to have penalties for particular person success.




